Treatment of sleep-disordered breathing in ENT
The treatment of sleep disordered breathing in ENT are largely operational measures. But due to the advancement of surgical techniques a painful and long recovery belongs to the past.
-
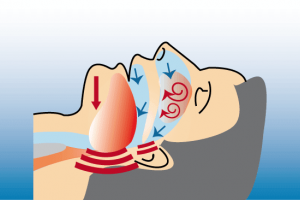
Anatomical changes in the nose, the soft palate or uvula can lead to restraint and turbulence in the air flow - a cause of snoring. -
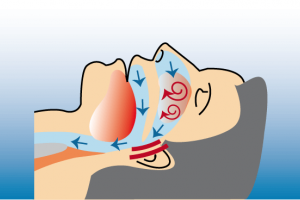
The air flow can be narrowed at different locations. Nose, soft palate with uvula and tongue base. The narrowing can cause not only annoying snoring but also dangerous breathing pauses. -
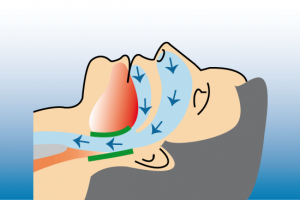
Normally, air can freely flow through the nose or mouth to the lungs.
In ENT, the treatment of sleep-disordered breathing focuses on two main areas. A distinction is made in the expansion of the airways in the nose and throat, and in the reduction of respiratory disability in the throat area.
The former belongs to the septoplasty, when the nasal septum is crooked, and the turbinate reduction, if they are too large.
If the tonsils are enlarged, the adenoidectomy is used, if the palatine tonsil is enlarged we us the tonsillectomy for their removal.
These resective surgery (removal of tissue) in ENT include the removal of polyps (growths) in the jaw and sinuses.
Often the causes of sleep-related breathing disorders are in excess tissue in the mouth. Here, the ENT is a specific type of therapy for any type of tissue modulating.
Do you have slackened and enlarged soft palate, a slackened and elongated uvula, with uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP), the excess tissue of the soft palate is removed with a scalpel. Furthermore, the soft palate is stiffened by appropriate incision and suture. Finally, in this procedure the uvula is shortened.
In laser-assisted Uvolopalatoplastic (LAUP) soft excess of the soft palate and the uvula (fluttering shares that may give rise to a snoring noise) is gently removed with a laser.
In general, this operation is performed ambulant under local anesthesia and the patient is finished after 15 minutes.
The RFA is organized accordingly. A needle-shaped applicator is inserted at the junction of the hard and soft palate, and advanced towards the palate base. The probe is heated by means of high frequency current, which leads to a degradation of the local tissue, which in the course becomes more rigid scar tissue.
